Audio Source Separation with NMF
Hello! This example demonstrates the use of Non-negative Matrix Factorization (NMF) for audio source separation, in the context of bioacoustics data (amphibean and whales).
This presentation is designed for the JJBA 2024 conference.
A tutorial (on AnuraSet) can be found at the following link: NMF for audio source separation.
Example on the Anuraset dataset
File: INCT17_20191113_040000. 3 estimated sources (according to the authors), hence NMF was performed with 3 components.
Original Audio
Separated Source 1
(Noise + grasshopper + constant bass frog)
Separated Source 2
(Frog)
Separated Source 3
(Bird)
Examples on marine mammals
This example is an underwater recordings containing humpback whales (TODO: ask Dorian Cazau for the reference).
The signal has been restricted to the first 12 minutes, for simplifying the problem and listening conditions.
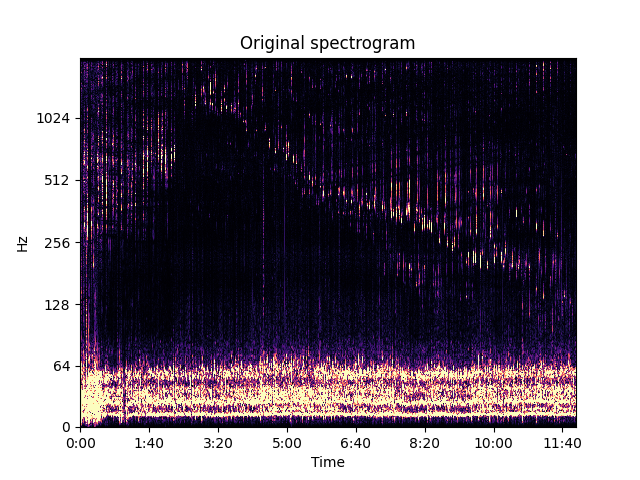
Below, you will find the original audio of the first 12 minutes, along with the spectrogram (STFT) of this audio.
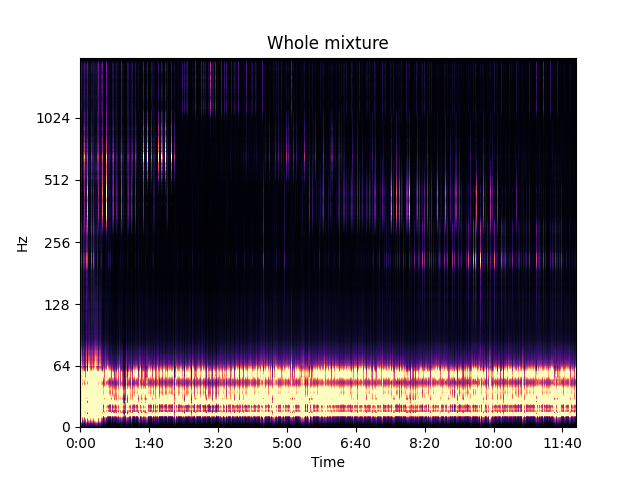
6 sources have been estimated by the authors, hence NMF was performed with 6 components. Find the results below. For the separated sources, only 10s with strong activity have been kept.
Note that for this example, NMF was computed using the Kullback-Leibler divergence
Original signal
Reconstructed mixture (with NMF)
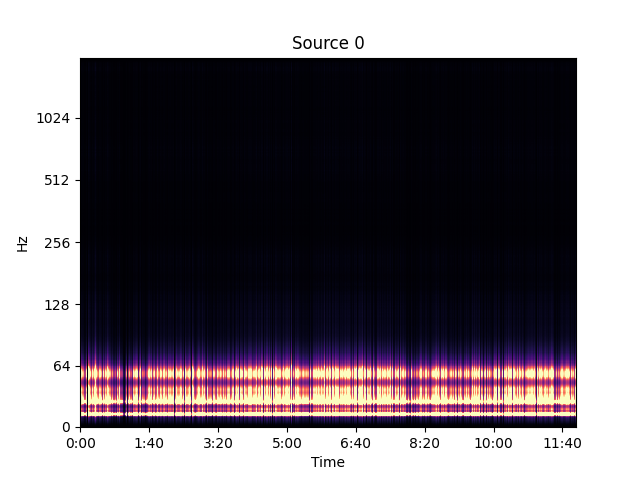
Separated Source 1
Background and water noise
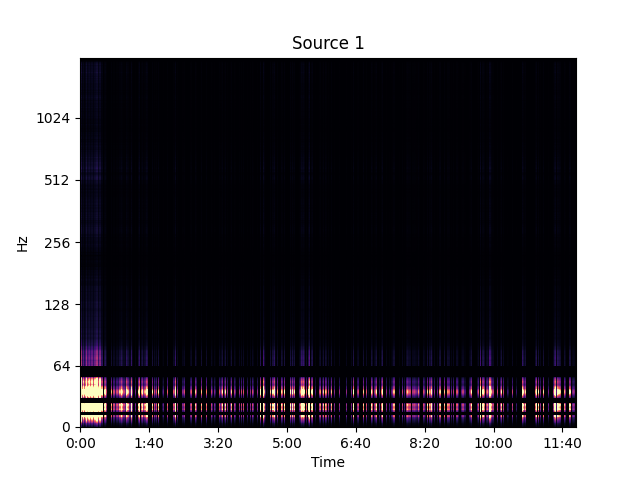
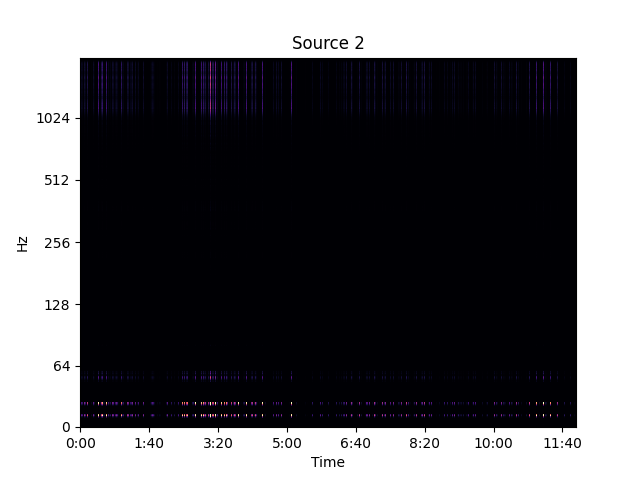
Separated Source 2
Low frequency call
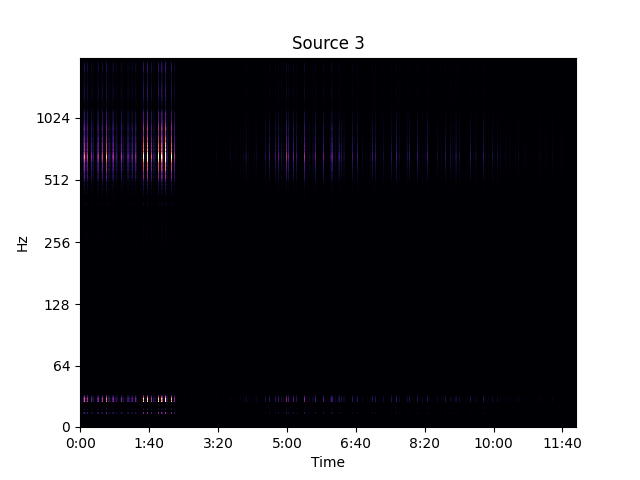
Separated Source 3
High frequency call
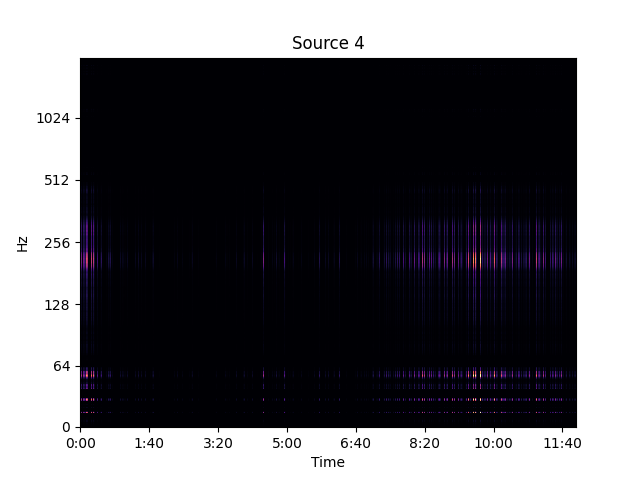
Separated Source 4
Medium-to-High frequency call
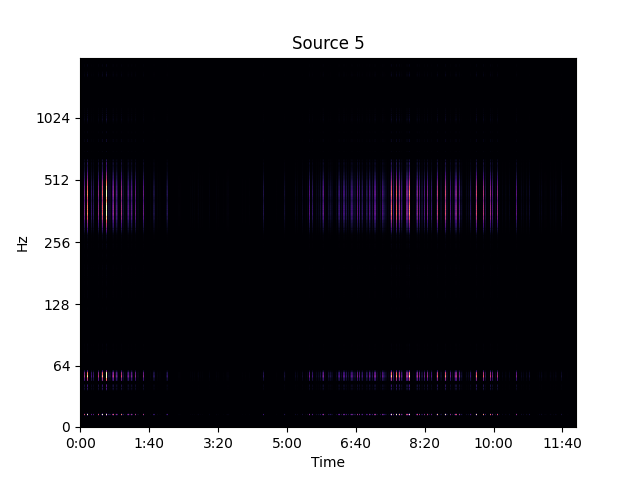
Separated Source 1
Medium-to-Low frequency call
Separated Source 1
Medium frequency call
intended